Topic how to calculate z score calculator: Looking to calculate a z-score? Our user-friendly calculator makes it easy to determine the z-score of a normal distribution. Simply input your raw score, population mean, and standard deviation, and hit \"Calculate Z\". Not sure how to convert between z-score and probability? Our calculator has you covered! Plus, if you\'re working with BMI, our tool can help you calculate the body mass index for patients between the ages of 2 and 20 years. Make your calculations a breeze with our efficient and accurate z-score calculator.
Table of Content
- How do I use a calculator to calculate z-scores?
- What is a z-score and why is it important in statistical analysis?
- How is the z-score calculated using a calculator?
- YOUTUBE: Finding the z-Score with TI 84+ Calculator
- What are the steps involved in calculating the z-score manually?
- How do you interpret the value of a z-score in relation to the mean and standard deviation?
- What is the purpose of calculating the z-score in probability distributions?
- How can the z-score be used to determine the probability between two z-scores?
- Are there any specific formulas or equations used for calculating the z-score on a calculator?
- Can the z-score be used to compare data from different populations?
- Are there any limitations or assumptions to consider when using the z-score calculator?
How do I use a calculator to calculate z-scores?
To calculate a z-score using a calculator, follow these steps:
1. Determine the raw score that you want to calculate the z-score for.
2. Identify the population mean and standard deviation for the dataset you are working with. These values are necessary to standardize the raw score into a z-score.
3. Open the calculator on your device, whether it is a physical calculator or an online calculator.
4. Look for the option or function on the calculator that allows you to input the raw score, population mean, and standard deviation.
5. Enter the raw score, population mean, and standard deviation into the appropriate fields on the calculator.
6. Press the \"Calculate\" or \"Z-Score\" button on the calculator, depending on the specific calculator you are using.
7. The calculator should then display the z-score associated with the raw score you provided.
Make sure to double-check your inputs and ensure that you are using the correct values for the population mean and standard deviation. Also, pay attention to any additional instructions or settings that may be specific to the calculator you are using.
READ MORE:
What is a z-score and why is it important in statistical analysis?
A z-score is a statistical measurement that indicates how far away a particular data point is from the mean of a distribution when measured in terms of standard deviations. It is important in statistical analysis because it allows us to compare and analyze data from different distributions by standardizing them onto a common scale.
To find the z-score of a data point, you can follow these steps:
1. Calculate the mean (μ) and standard deviation (Ï) of the distribution that the data point belongs to.
2. Subtract the mean (μ) from the data point.
3. Divide the result by the standard deviation (Ï).
The formula for calculating the z-score is: z = (x - μ) / Ï
The resulting z-score represents the number of standard deviations the data point is away from the mean. A positive z-score indicates that the data point is above the mean, while a negative z-score indicates that it is below the mean.
The z-score is useful in statistical analysis for various reasons:
1. Standardization: By converting data points into z-scores, we can compare and analyze data from different distributions that may have different means and standard deviations. This allows us to make meaningful comparisons across different datasets.
2. Outlier detection: Z-scores can be used to identify outliers in a dataset. Any data point with a z-score that falls outside a certain threshold (often set at ±3) may be considered an outlier.
3. Probability calculation: Z-scores are also helpful in calculating probabilities associated with a particular value within a distribution. By converting a value into a z-score, we can determine the likelihood of obtaining that value or a more extreme value in the distribution.
Overall, z-scores provide a standardized way to understand and analyze data in statistical analysis, enabling comparisons, identification of outliers, and calculation of probabilities.
How is the z-score calculated using a calculator?
To calculate the z-score using a calculator, you will typically need the following information:
1. Raw score: This is the value for which you want to calculate the z-score.
2. Population mean: This is the average value of the population the raw score belongs to.
3. Standard deviation: This measures the variability or spread of the population data.
Here are the steps to calculate the z-score using a calculator:
1. Find the difference between the raw score and the population mean.
z = (raw score - population mean)
2. Divide the difference by the standard deviation.
z = (raw score - population mean) / standard deviation
3. Use the calculator to perform the division and calculate the value of z.
4. Round the z-score to the desired number of decimal places if needed.
The resulting value of z is the z-score. It tells you how many standard deviations the raw score is from the population mean. A positive z-score indicates that the raw score is above the mean, while a negative z-score indicates that the raw score is below the mean.
Finding the z-Score with TI 84+ Calculator
Want to understand how to measure the variability of data in statistics? Look no further! Our captivating video on z-scores will break down this concept in a simple and engaging way, ensuring that you grasp all the essential knowledge and feel confident in your data analysis skills. Join us now for an enlightening journey into the world of z-scores!
What are the steps involved in calculating the z-score manually?
To calculate the z-score manually, follow these steps:
1. Start by determining the raw score that you want to calculate the z-score for.
2. Obtain the population mean, which is the average value of the entire population that the raw score belongs to.
3. Determine the population standard deviation, which measures the spread of the data points in the population.
4. Calculate the z-score using the formula:
z = (raw score - population mean) / population standard deviation
This formula calculates the number of standard deviations the raw score is away from the mean.
5. Once you have calculated the z-score using the formula, you will have a numerical value. This value represents the distance between the raw score and the mean in terms of standard deviations.
6. The positive or negative sign of the z-score indicates whether the raw score is above or below the mean, respectively.
7. The magnitude of the z-score represents the number of standard deviations the raw score is away from the mean. A larger magnitude indicates a greater distance from the mean.
8. Interpret the z-score by comparing it to a standard normal distribution table or using a z-score to probability calculator. This will help determine the percentage of data points that fall below or above the raw score. A positive z-score corresponds to a percentile above the mean, while a negative z-score corresponds to a percentile below the mean.
9. Remember, a z-score of 0 means the raw score is exactly at the mean, a positive z-score indicates a value above the mean, and a negative z-score indicates a value below the mean.
10. Finally, use the z-score to make inferences about the raw score\'s position within the population distribution or compare it to other z-scores.
By following these steps, you can manually calculate the z-score for any given raw score. However, it is often more convenient to use online calculators or statistical software to perform these calculations.
How do you interpret the value of a z-score in relation to the mean and standard deviation?
A z-score represents the number of standard deviations a particular data point is away from the mean of a distribution. It indicates the relative position of a data point within the distribution.
To interpret the value of a z-score in relation to the mean and standard deviation, follow these steps:
1. Determine the mean (μ) and standard deviation (Ï) of the distribution.
2. Calculate the z-score using the formula:
z = (x - μ) / Ï
where x is the data point you want to calculate the z-score for.
3. Once you have the z-score, you can interpret it in the following ways:
a. A positive z-score indicates that the data point is above the mean, while a negative z-score indicates that it is below the mean.
b. A z-score of 0 means the data point is equal to the mean.
c. The magnitude of the z-score represents how far the data point is from the mean in terms of standard deviations. A larger absolute value of the z-score indicates a greater distance from the mean.
d. Comparing z-scores between different data points allows you to determine which data point is relatively higher or lower than the other in the distribution. The greater the difference in z-scores, the greater the difference in the data points\' positions within the distribution.
e. Using z-tables or statistical software, you can find the corresponding percentile or probability associated with a z-score. This provides information on where the data point falls within the distribution.
Overall, the z-score allows you to standardize and compare data points across different distributions, helping to understand their relative position and significance.

_HOOK_
What is the purpose of calculating the z-score in probability distributions?
The purpose of calculating the Z-score in probability distributions is to find out how many standard deviations a particular data point or observation is from the mean of the distribution. It is a way to standardize and compare data in different distributions.
By calculating the Z-score, we can determine the relative position of a data point in a distribution and understand its significance in terms of its deviation from the mean. A positive Z-score indicates that the data point is above the mean, while a negative Z-score indicates that it is below the mean.
The Z-score calculation involves subtracting the mean of the distribution from the data point and then dividing the result by the standard deviation. The formula for calculating the Z-score is:
Z = (X - μ) / Ï
where:
Z is the Z-score,
X is the data point,
μ is the mean of the distribution, and
Ï is the standard deviation of the distribution.
Once we have calculated the Z-score, we can use it to determine various probabilities associated with the data point. For example, we can find the probability of obtaining a certain value or a more extreme value from the distribution. This probability is usually represented as a percentage or a decimal.
The Z-score is also helpful in comparing data from different distributions. Since it standardizes the data by converting it into a common scale, we can compare observations from different distributions and understand how they differ in relation to their respective means and standard deviations.
Overall, calculating the Z-score allows us to interpret data in probability distributions, understand its relative position, and make comparisons across different distributions. It is a useful tool in statistical analysis and decision-making processes.
Finding Probability with z-Score using Casio fx 991ms Calculator
Dive into the fascinating realm of probability with our eye-opening video! If you want to unravel the mysteries behind chance and uncertainty and learn how to make informed predictions, this video is just what you need. With clear explanations and practical examples, we\'ll help you master the art of probability and unlock a new level of understanding. Don\'t miss out!
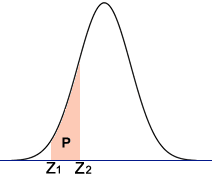
How can the z-score be used to determine the probability between two z-scores?
To determine the probability between two z-scores using the z-score, you can follow these steps:
1. Identify the two z-scores for which you want to find the probability between.
2. Use a z-table or a z-score calculator to find the corresponding probabilities for each z-score. This involves looking up the z-scores in the table or entering them into the calculator to obtain the associated probabilities.
3. Subtract the probability corresponding to the lower z-score from the probability corresponding to the higher z-score. This will give you the probability between the two z-scores.
For example, let\'s say you have two z-scores: z1 = 1.5 and z2 = 2.0.
Using a z-table or a z-score calculator, you find that the corresponding probabilities for these z-scores are: P(z1) = 0.9332 and P(z2) = 0.9772.
To find the probability between these two z-scores, subtract the probability of z1 from the probability of z2:
P(z1 < X < z2) = P(z2) - P(z1)
= 0.9772 - 0.9332
= 0.044
Therefore, the probability of a value falling between z1 = 1.5 and z2 = 2.0 is 0.044 or 4.4%.
Note: This calculation assumes a standard normal distribution (mean = 0 and standard deviation = 1). If you have a different mean and standard deviation, you need to standardize the values using the formula z = (X - mean) / standard deviation before proceeding with the calculation.

Are there any specific formulas or equations used for calculating the z-score on a calculator?
Yes, there are specific formulas or equations used for calculating the z-score on a calculator. The z-score formula is given by:
z = (x - μ) / Ï
Where:
- z is the z-score
- x is the raw score
- μ is the population mean
- Ï is the standard deviation
To calculate the z-score using a calculator, you would typically follow these steps:
1. Input the raw score (x).
2. Input the population mean (μ).
3. Input the standard deviation (Ï).
4. Subtract the population mean from the raw score: (x - μ).
5. Divide the result by the standard deviation: (x - μ) / Ï.
6. Press the \"Calculate\" or \"Compute\" button to obtain the z-score.
The z-score represents how many standard deviations a raw score is from the population mean. It helps in determining the relative position or significance of a data point within a distribution. Whether you use an online calculator or a physical calculator, the process remains the same â you input the required values, perform the calculations, and obtain the z-score.
Can the z-score be used to compare data from different populations?
Yes, the z-score can be used to compare data from different populations. The z-score is a measure of how many standard deviations a particular data point is away from the mean of a population. By standardizing the data using the z-score, we can compare observations from different populations on a common scale.
To use the z-score to compare data from different populations, you can follow these steps:
1. Gather the data from each population that you want to compare.
2. Calculate the mean and standard deviation for each population.
3. Select a specific data point from one of the populations that you want to compare.
4. Calculate the z-score for that data point using the formula:
z = (x - μ) / Ï
Where x is the value of the data point, μ is the mean of the population, and Ï is the standard deviation of the population.
5. Repeat step 4 for each data point you want to compare.
6. Compare the z-scores calculated for the different data points. A higher positive z-score means the data point is above the mean compared to the population, while a lower negative z-score means the data point is below the mean compared to the population.
By comparing the z-scores, you can determine how different or similar a particular data point is compared to the corresponding population mean. However, it\'s important to note that comparing data from different populations using z-scores assumes that the populations follow a normal distribution or at least have similar characteristics.

Are there any limitations or assumptions to consider when using the z-score calculator?
When using a z-score calculator, there are a few limitations and assumptions to consider:
1. Normally distributed data: The z-score assumes that the data you are working with follows a normal distribution. If your data is not normally distributed, the z-score may not be an appropriate measure to use.
2. Independence of observations: The calculation of the z-score assumes that each observation is independent of the others. If there is dependence between the observations, it may affect the accuracy of the z-score calculation.
3. Sample size: The z-score is more reliable when computed using a larger sample size. As the sample size decreases, the accuracy of the z-score calculation may decrease as well.
4. Known population parameters: The z-score calculation assumes that you have access to the population mean and standard deviation. In many cases, these parameters are estimated from a sample. If your sample size is small or if you are using estimated parameters, the accuracy of the z-score calculation may be affected.
5. Outliers: The presence of outliers in the data can influence the z-score calculation. Outliers can heavily skew the results and affect the accuracy of the z-score, especially with small sample sizes.
6. Homogeneity of variances: When comparing groups using z-scores, it is assumed that the groups have similar variances. If the variances differ significantly, using z-scores may not be appropriate.
It is important to consider these limitations and assumptions when using a z-score calculator to ensure accurate and meaningful results.
_HOOK_

