Topic How to find z score between two numbers: Finding the z-score between two numbers is an essential statistical calculation that helps determine the probability of an event occurring. By calculating the z-score, one can assess the relative position of a data point within a standard distribution. With this valuable information, researchers and analysts can make informed decisions and draw meaningful conclusions from their data. Understanding how to find the z-score between two numbers empowers individuals to interpret data accurately and unlocks the potential for robust statistical analysis.
Table of Content
- How to calculate the z-score between two numbers?
- What is a z-score?
- How does the z-score indicate the position of a data point relative to the mean?
- YOUTUBE: Standard Normal Table: Area Between Two Z-Scores
- What does a z-score of 0 represent on the standard normal distribution graph?
- How can I calculate the area between two z-scores?
- What are left and right bound z-scores, and how are they used to calculate the area between two z-scores?
- Can you provide step-by-step instructions on how to split z-scores after the tenths place?
- Why is it important to split z-scores in certain cases?
- How do I find the z-score of a data point between two given z-scores?
- Are there any specific formulas or calculations involved in finding the z-score between two numbers?
How to calculate the z-score between two numbers?
To calculate the z-score between two numbers, you need to follow these steps:
1. Determine the mean and standard deviation of the distribution to which the numbers belong. The mean represents the average value, and the standard deviation measures the dispersion or spread of the data around the mean.
2. Subtract the mean from each of the two numbers; this step is known as \"standardizing\" the values.
3. Divide the resulting value by the standard deviation. This division helps to scale the data and express it in terms of standard deviations from the mean.
4. The resulting values are the z-scores for each of the two numbers. A positive z-score indicates that the number is above the mean, while a negative z-score means it is below the mean.
Note: The z-score describes the position of a data point in relation to the mean, measured in terms of standard deviations. It allows for the comparison and interpretation of data across different distributions.
READ MORE:
What is a z-score?
A z-score, also known as a standard score, measures the distance between a data point and the mean of a distribution in terms of standard deviations. It tells you how many standard deviations a particular value is away from the mean.
The formula for calculating the z-score is:
z = (x - μ) / Ï
Where:
- x is the value you are interested in,
- μ is the mean of the distribution, and
- Ï is the standard deviation of the distribution.
To calculate the z-score, you subtract the mean from the data point and divide the result by the standard deviation. This normalization process allows you to compare different data points from different distributions on a standardized scale.
The interpretation of the z-score is as follows:
- A positive z-score means the data point is above the mean.
- A negative z-score means the data point is below the mean.
- A z-score of 0 indicates that the data point is identical to the mean.
The significance of the z-score lies in its ability to determine the relative position of a data point within a distribution. It helps in understanding how unusual or typical a particular value is when compared to the rest of the data.
How does the z-score indicate the position of a data point relative to the mean?
The z-score, also known as the standard score, is a statistical measurement that indicates the position of a data point relative to the mean of a distribution. It tells us how many standard deviations a particular data point is away from the mean.
To calculate the z-score for a specific data point, you can use the formula:
z = (x - μ) / Ï
where:
- z is the z-score
- x is the data point you want to calculate the z-score for
- μ is the mean of the distribution
- Ï is the standard deviation of the distribution
Once you have calculated the z-score using this formula, you can interpret its value to understand the position of the data point relative to the mean.
A positive z-score indicates that the data point is above the mean, while a negative z-score indicates that the data point is below the mean. The absolute value of the z-score tells you how many standard deviations away the data point is from the mean.
For example, if you have a z-score of 2, it means that the data point is two standard deviations above the mean. Conversely, a z-score of -1 would indicate that the data point is one standard deviation below the mean.
The z-score can be helpful in understanding the significance or outliers in a dataset. Data points with extreme positive or negative z-scores (e.g., z-scores greater than 2 or less than -2) are considered to be outliers and may warrant further investigation.
Overall, the z-score is a standardized way to indicate the relative position of a data point within a distribution, based on its distance from the mean.
Standard Normal Table: Area Between Two Z-Scores
Want to understand z-scores and their significance? Watch this video that simplifies the concept and demonstrates how to calculate z-scores step-by-step. Improve your statistical analysis skills and gain a deeper understanding of data interpretation. Don\'t miss out on this informative video!
What does a z-score of 0 represent on the standard normal distribution graph?
A z-score of 0 on the standard normal distribution graph represents the point that is exactly at the mean of the distribution. In other words, it indicates that the value is equal to the average value of the dataset being analyzed.
The standard normal distribution graph is a bell-shaped curve that represents a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. This graph is commonly used in statistics to analyze and compare data.
The z-score is a way to measure the distance of a data point from the mean in terms of standard deviations. The formula to calculate the z-score is (x - mean) / standard deviation, where x is the data point, mean is the average, and standard deviation is a measure of the spread of the data.
When the z-score is 0, it means that the data point is exactly at the mean. This implies that the data point has no deviation from the average value of the dataset. It is neither above nor below the mean, but at the center of the distribution.
In practical terms, a z-score of 0 can be interpreted as a neutral or average value. It signifies that the data point is neither unusually high nor unusually low when compared to the rest of the dataset. It is a reference point from which other z-scores can be compared to determine the relative position of data points in the distribution.
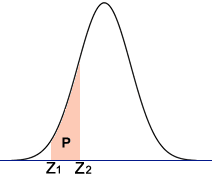
How can I calculate the area between two z-scores?
To calculate the area between two z-scores, you can follow these steps:
1. Identify the z-scores: Determine the values of the two z-scores between which you want to calculate the area.
2. Standardize the z-scores: If your z-scores are not already in standard form, convert them to standard form by subtracting the mean and dividing by the standard deviation of the distribution.
3. Find the cumulative probabilities: Use a Z-Score table or a calculator with a normal distribution function to find the cumulative probability (area) associated with each of the standardized z-scores. This gives you the area to the left of each z-score.
4. Calculate the difference: Subtract the smaller cumulative probability (area) from the larger cumulative probability (area) to find the area between the two z-scores.
Let\'s illustrate these steps with an example:
Suppose you have two z-scores, z1 = 1.5 and z2 = 2.2.
Step 1: Identify the z-scores: z1 = 1.5, z2 = 2.2.
Step 2: Standardize the z-scores: Assuming a standard normal distribution, no standardization is required as the z-scores are already in standard form.
Step 3: Find the cumulative probabilities: Using a Z-Score table or a calculator, you can find the cumulative probability associated with each z-score:
Cumulative probability for z1 = 1.5: P(Z ⤠1.5) = 0.9332.
Cumulative probability for z2 = 2.2: P(Z ⤠2.2) = 0.9857.
Step 4: Calculate the difference: Subtract the smaller cumulative probability from the larger cumulative probability to find the area between the two z-scores:
Area between z1 and z2 = P(z1 ⤠Z ⤠z2) = P(Z ⤠2.2) - P(Z ⤠1.5) = 0.9857 - 0.9332 = 0.0525.
Therefore, the area between z-scores 1.5 and 2.2 is 0.0525. This represents the probability of obtaining a z-score within that range under the standard normal distribution.
_HOOK_
What are left and right bound z-scores, and how are they used to calculate the area between two z-scores?
Left and right bound z-scores are used to calculate the area between two z-scores in a standard normal distribution.
In a standard normal distribution, the mean is represented by a z-score of 0, and the distribution follows a bell-shaped curve. The area under the curve represents the probability of a particular value occurring.
To calculate the area between two z-scores, first, you need to determine the left bound z-score and the right bound z-score. The left bound z-score refers to the z-score to the left of the desired area, and the right bound z-score refers to the z-score to the right of the desired area.
To find the left bound z-score, you can subtract the desired area from 0.5 and then find the corresponding z-score using a standard normal distribution table or a calculator. The left bound z-score is the negative value of this z-score.
To find the right bound z-score, subtract the left bound z-score from the desired area and again use a standard normal distribution table or calculator to find the corresponding z-score.
Once you have the left and right bound z-scores, you can calculate the area between them by subtracting the left bound z-score area from the right bound z-score area. This will give you the probability or area between the two z-scores.
It\'s important to note that these calculations assume a standard normal distribution, where the mean is 0 and the standard deviation is 1. If you are working with a different normal distribution with a different mean or standard deviation, additional adjustments may be necessary.
Finding Area Between Two Z-Scores
Curious about how to calculate the area under a curve? This video will guide you through the process, explaining the importance of area in various disciplines. Learn how to find the area using different techniques and enhance your knowledge in a visually engaging way. Watch it now and expand your mathematical prowess!
Standard Normal Distribution Tables, Z Scores, Probability & Empirical Rule - Stats
Dive into the world of the standard normal distribution with this video that breaks down its fundamental concepts. Understand the properties, characteristics, and implications of this widely used distribution. Gain insights into how it relates to real-life scenarios and refine your statistical knowledge. Prepare to unravel the secrets of the standard normal distribution!
Can you provide step-by-step instructions on how to split z-scores after the tenths place?
To split z-scores after the tenths place, you can follow these step-by-step instructions:
1. Start with the given z-scores. Let\'s say you have two z-scores, such as 1.95 and 2.13.
2. Look at the tenths place of each z-score. In this case, the tenths place of 1.95 is 9, and the tenths place of 2.13 is 1.
3. Now, split each z-score into two parts: the whole number part and the decimal part.
4. For the z-score 1.95, the whole number part is 1 and the decimal part is 0.95. Similarly, for the z-score 2.13, the whole number part is 2 and the decimal part is 0.13.
5. After splitting the z-scores, you can add or subtract (depending on the context) the tenths place from the whole number part. In this case, since we want to split the z-scores after the tenths place, we will add the tenths place to the whole number part.
6. For the z-score 1.95, add the tenths place 0.9 to the whole number part 1, which gives you 1.9 as the first split z-score.
7. For the z-score 2.13, add the tenths place 0.1 to the whole number part 2, which gives you 2.1 as the second split z-score.
So, after splitting the given z-scores 1.95 and 2.13 after the tenths place, you have 1.9 and 2.1 respectively.
Please note that splitting z-scores after the tenths place is not a standard statistical procedure but can be useful in some specific contexts or calculations.

Why is it important to split z-scores in certain cases?
It is important to split z-scores when calculating the probability or area under the normal distribution curve between two specific z-scores. This is necessary because the standard normal distribution table (also known as the z-table) provides probabilities for specific z-scores up to two decimal places.
The z-scores represent the number of standard deviations a particular data point is away from the mean. Since the standard normal distribution is symmetric around the mean, the area under the curve between two z-scores represents the probability of a random variable falling between those two values.
However, the z-table only provides probabilities for specific z-scores, usually up to two decimal places. When calculating the area between two z-scores, it is necessary to split the z-scores after the tenths place (one decimal place) and use the corresponding table values.
For example, if we have z-scores of 1.95 and 2.13, we would split them as follows: 1.9 + 0.05 and 2.1 + 0.03. We then look up the corresponding probabilities for 1.9, 2.0, and 2.1 from the z-table. These probabilities represent the area under the normal distribution curve between the specific z-scores.
By splitting the z-scores and using the appropriate table values, we can accurately calculate the probability or area under the normal distribution curve between two given z-scores. This is important in various statistical calculations, hypothesis testing, and making informed decisions based on the distribution of data.
How do I find the z-score of a data point between two given z-scores?
To find the z-score of a data point between two given z-scores, you can follow these steps:
Step 1: Determine the left and right z-scores of the interval. Let\'s say the left z-score is denoted as z1 and the right z-score as z2.
Step 2: Find the cumulative probability associated with the left z-score (z1) using a z-table or a statistical calculator. This refers to the area to the left of z1 under the standard normal curve.
Step 3: Find the cumulative probability associated with the right z-score (z2) using the same method as in Step 2. This refers to the area to the left of z2 under the standard normal curve.
Step 4: Calculate the area between z1 and z2 by subtracting the cumulative probability of z1 from the cumulative probability of z2. This will give you the proportion of the distribution that lies between z1 and z2.
Step 5: Finally, convert the obtained area between z1 and z2 to a z-score (let\'s call it z3) by looking up the area in a z-table or using a statistical calculator. This gives you the z-score corresponding to the data point between the two given z-scores.
Note: If you have the z-scores rounded to a certain decimal place, make sure to adjust the z-scores accordingly by incorporating the decimal portion as shown in the third search result.
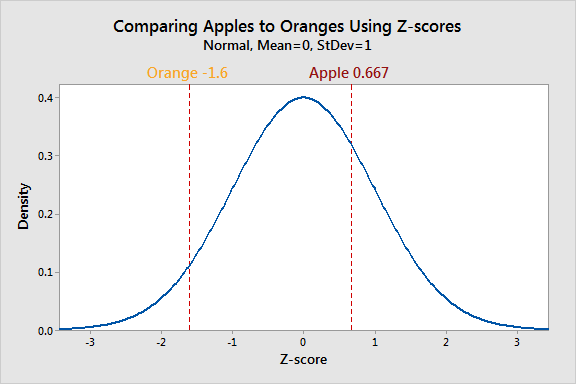
Are there any specific formulas or calculations involved in finding the z-score between two numbers?
To find the z-score between two numbers, you need to calculate the z-scores for each individual number and then find the difference between them.
Step 1: Calculate the z-scores for each number using the formula:
z = (x - μ) / Ï
In this formula:
- x represents the individual number you are calculating the z-score for.
- μ is the mean of the distribution.
- Ï is the standard deviation of the distribution.
Step 2: Subtract the z-score of the smaller number from the z-score of the larger number. This will give you the z-score between the two numbers.
Let\'s take an example to illustrate this process:
Suppose you have two numbers, x1 = 10 and x2 = 20, and you want to find the z-score between them.
Step 1: Calculate the z-scores for each number:
z1 = (x1 - μ) / Ï
z2 = (x2 - μ) / Ï
Step 2: Subtract the smaller z-score from the larger z-score:
z = z2 - z1
It\'s important to note that you need to have the mean and standard deviation of the distribution in order to calculate the z-scores accurately.
Remember, the z-score measures the number of standard deviations an individual data point is from the mean of the distribution. So, by calculating the z-score between two numbers, you are essentially finding the difference in their positions relative to the mean.
_HOOK_
Normal Distribution: Calculating Probabilities (z-table)
Uncertain about probabilities and how they influence outcomes? This video will demystify the topic and empower you with the skills to calculate probabilities accurately. Explore real-world scenarios and learn practical applications of probabilities in fields such as finance, science, and sports. Don\'t miss this opportunity to enhance your decision-making abilities through understanding probabilities.


