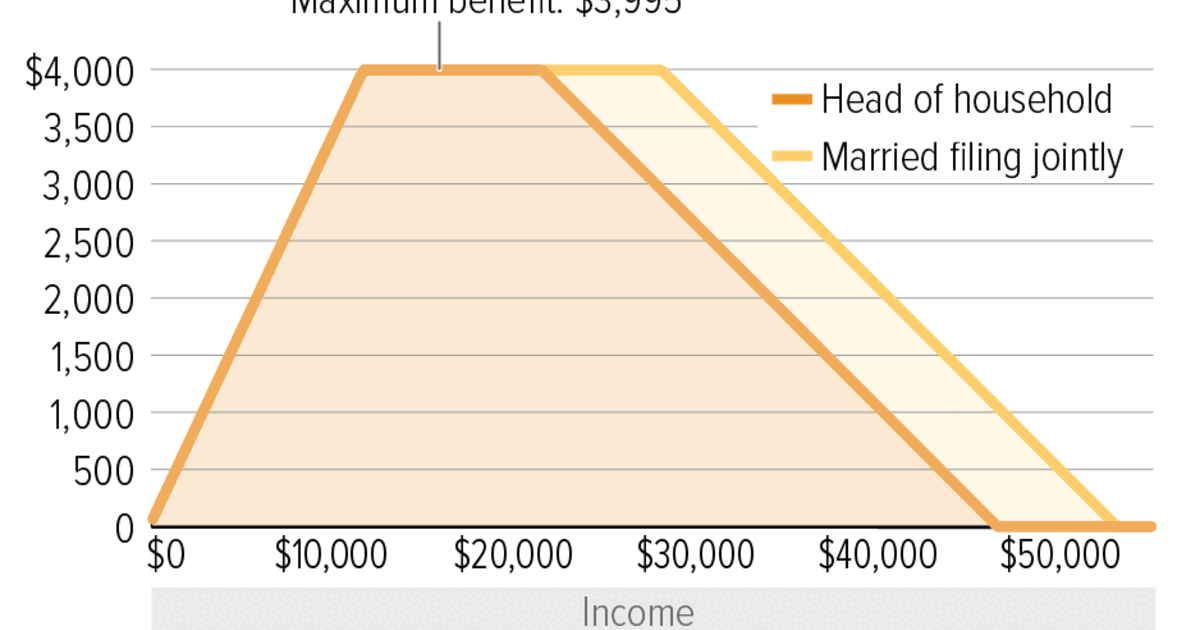Topic what is negative income tax: Negative income tax is a progressive system that aims to support individuals with lower incomes by providing them with financial assistance. Unlike traditional taxes, this approach reverses the direction in which taxes are paid for those below a certain income threshold. With the potential to replace welfare programs, negative income tax offers refundable credits, ensuring a basic income guarantee for eligible taxpayers. This innovative approach fosters economic equality and empowers individuals to meet their needs and pursue their aspirations.
Table of Content
- What are the key features of a negative income tax system?
- What is the concept of a negative income tax?
- How does a negative income tax system reverse the direction of tax payment?
- YOUTUBE: Milton Friedman - The Negative Income Tax
- What is the purpose of providing money to individuals below a certain income level through a negative income tax?
- How does negative income tax differ from traditional welfare programs?
- What are the potential benefits of implementing a negative income tax system?
- Are there any countries that currently utilize a negative income tax system?
- How does a negative income tax proposal suggest replacing welfare with refundable tax credits?
- What is the basic income guarantee and how does it relate to negative income tax?
- What are some potential criticisms or challenges associated with implementing a negative income tax system?
What are the key features of a negative income tax system?
The key features of a negative income tax system are as follows:
1. Reverse Tax Payments: The central feature of a negative income tax system is that it reverses the direction of tax payments for individuals with incomes below a specific threshold. Instead of paying taxes to the government, these individuals receive money from the government in the form of a tax credit.
2. Income Threshold: The negative income tax system sets a specific income threshold below which individuals qualify for the tax credit. This threshold is typically determined based on the poverty line or a certain percentage above it.
3. Gradual Reduction: As an individual\'s income increases above the threshold, the tax credit gradually reduces until it reaches zero. This gradual reduction ensures that individuals are incentivized to earn more income without abruptly losing all the benefits.
4. Income Supplement: The negative income tax acts as an income supplement for low-income individuals and families. It provides them with additional funds to meet their basic needs and alleviate poverty.
5. Simplified Administration: Implementing a negative income tax system can simplify the administration of social welfare programs. Instead of having multiple welfare programs with different eligibility criteria and bureaucracies, a single tax credit can be provided to those below the income threshold.
6. Incentive to Work: By gradually reducing the tax credit as income increases, a negative income tax system provides a strong incentive for individuals to seek employment or increase their work hours. This helps to address the issue of welfare dependency and encourages self-sufficiency.
7. Cost Adjustments: The cost of implementing a negative income tax system can be adjusted by determining the tax credit rate and income threshold. These parameters need to be carefully calibrated to strike a balance between providing adequate support to low-income individuals and minimizing the cost to the government.
8. Poverty Reduction: The primary objective of a negative income tax system is to reduce poverty and income inequality by ensuring a minimum level of income for those below the income threshold. By directly targeting the needy population, it offers a more efficient way of reducing poverty compared to universal welfare programs.
Overall, a negative income tax system is designed to address poverty and income inequality by providing financial assistance to low-income individuals and families in a way that promotes work incentives and simplifies the administration of social welfare programs.

READ MORE:
What is the concept of a negative income tax?
The concept of a negative income tax is a government policy that aims to provide financial assistance to individuals or families below a certain income level. Instead of taxing these individuals, as is the case with traditional income tax systems, the negative income tax system actually provides them with money.
Here is a step-by-step breakdown of the concept:
1. Income Threshold:
- The negative income tax system sets a specific income threshold. Individuals or families whose income falls below this threshold are eligible to receive assistance.
2. Income Redistribution:
- Under this system, individuals or families with incomes below the threshold receive financial support from the government in the form of a negative tax. This means that instead of paying taxes, they actually receive money from the government to supplement their income.
3. Gradual Reduction:
- As income increases above the threshold, the amount of financial assistance provided gradually decreases. A predetermined rate is applied to reduce the amount of the negative tax as income rises.
4. Threshold Phasing Out:
- Above a certain income level, typically higher than the threshold, the negative income tax assistance completely phases out and individuals or families become responsible for paying their taxes like any other taxpayer.
The ultimate goal of a negative income tax is to provide a safety net for individuals or families with low incomes, reducing poverty and ensuring a minimum level of income for all members of society. It aims to alleviate financial burdens, encourage workforce participation, and promote economic stability.
How does a negative income tax system reverse the direction of tax payment?
A negative income tax system reverses the direction in which tax is paid for incomes below a certain level. Here is a step-by-step explanation of how it works:
1. Traditional income tax: In a traditional income tax system, individuals with higher incomes are taxed at higher rates, while those with lower incomes pay lower or no taxes.
2. Threshold income level: In a negative income tax system, there is a designated income threshold below which individuals do not have to pay any taxes.
3. Tax credit: Instead of paying taxes, individuals with incomes below the threshold receive tax credits. These tax credits are designed to provide financial assistance to those with lower incomes.
4. Gradual reduction: As individuals earn income above the threshold, the tax credits gradually reduce, eventually reaching zero. This means that individuals will start paying taxes as their income exceeds the threshold.
5. Simplicity and efficiency: The negative income tax system aims to simplify the tax structure and reduce administrative burden by providing direct financial assistance to those in need. It also encourages work and entrepreneurship since individuals can retain a portion of their earnings without losing all of the benefits.
6. Welfare replacement: The negative income tax system is often proposed as a way to replace or reform existing welfare programs. By providing a guaranteed basic income through the tax credits, it aims to address poverty and inequality more efficiently.
Overall, a negative income tax system reverses the direction of tax payment by eliminating taxes for individuals below a certain income level and providing them with tax credits instead. This approach seeks to alleviate financial strain on lower-income individuals and create a simpler and more efficient way of addressing poverty and income inequality.
Milton Friedman - The Negative Income Tax
Explore the brilliant mind of economist Milton Friedman as he delves into the concept of the Negative Income Tax. In this captivating video, Friedman explains how this unique approach to income redistribution can pave the way for a fairer society and stronger economy. Don\'t miss the chance to gain valuable insights from one of the greatest economic thinkers of our time.
Negative Income Tax
Are you tired of the burdensome income tax system? Discover an innovative alternative - the Negative Income Tax. This groundbreaking video breaks down how this progressive taxation method can effectively uplift individuals and families in need while reducing the strain on the middle class. Say goodbye to complex tax calculations, and hello to a more equitable society.
What is the purpose of providing money to individuals below a certain income level through a negative income tax?
The purpose of providing money to individuals below a certain income level through a negative income tax is to address poverty and inequality in society.
Here is a step-by-step explanation:
1. Ensuring basic needs: The primary purpose of a negative income tax is to ensure that individuals below a certain income level have enough money to meet their basic needs, such as food, shelter, and healthcare. By providing financial assistance, it aims to alleviate poverty and reduce social and economic disparities.
2. Promoting social welfare: By providing financial support to low-income individuals, a negative income tax aims to improve overall social welfare. It recognizes that individuals with lower incomes often face significant challenges in meeting their basic needs and that financial assistance can have a positive impact on their lives.
3. Encouraging work incentivization: In contrast to traditional welfare programs that can create disincentives for individuals to work, a negative income tax is designed to provide incentives for work. By reducing the tax burden or providing direct cash transfers, individuals are motivated to earn income and participate in the workforce, ultimately reducing dependency on government assistance.
4. Simplifying the welfare system: Another purpose of a negative income tax is to simplify the welfare system. Instead of having multiple welfare programs with varying eligibility criteria and complex bureaucracy, a negative income tax consolidates these programs into a single system. This simplification reduces administrative costs and ensures that the assistance reaches those who need it most effectively.
5. Enhancing social mobility: Providing income support to individuals below a certain income level can help break the cycle of poverty and enhance social mobility. By giving people the means to meet their basic needs, a negative income tax can give them the opportunity to pursue education, training, or better employment prospects, enabling them to move up the economic ladder.
Overall, the purpose of providing money to individuals below a certain income level through a negative income tax is to promote equality, alleviate poverty, and create an environment that encourages work and social mobility.
How does negative income tax differ from traditional welfare programs?
Negative income tax (NIT) differs from traditional welfare programs in several ways:
1. Income Limit: Traditional welfare programs often have strict income limits, which means that individuals above a certain income threshold are not eligible for benefits. However, NIT is designed to provide assistance to low-income individuals and families regardless of their income level, albeit in a reduced amount as income rises.
2. Cash Transfer: NIT provides cash transfers directly to individuals or households based on their income level. It aims to supplement the income of those who earn below a certain threshold, rather than tying assistance to specific goods or services. This approach gives individuals more flexibility in how they utilize the funds, allowing them to address their most pressing needs.
3. Gradual Reduction: With traditional welfare programs, benefits are often abruptly eliminated once an individual\'s income exceeds a certain threshold. This can create disincentives for individuals to increase their earnings since the loss of benefits can outweigh the additional income earned. In contrast, NIT gradually reduces the amount of assistance as income rises, ensuring that individuals always have an incentive to increase their earnings.
4. Simplified Administration: Traditional welfare programs can be complex and bureaucratic, requiring significant administrative resources to determine eligibility and distribute benefits. NIT, on the other hand, simplifies the process by integrating the benefits into the tax system. Eligibility and benefit amounts are determined through the individual\'s tax return, reducing administrative costs and improving efficiency.
5. Negative Tax Rate: NIT introduces the concept of a negative tax rate, where individuals with incomes below the threshold receive a payment from the government instead of paying taxes. This allows the tax system to be used as a mechanism for income redistribution, providing support directly to those who need it most.
Overall, NIT offers a more flexible, simplified, and incentive-aligned approach compared to traditional welfare programs. By providing direct cash transfers, gradually reducing benefits, and simplifying administration, NIT aims to alleviate poverty and encourage individuals to increase their earnings without fear of losing crucial assistance.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/close-up-hands-of-businessman-working-with-business-document-and-laptop-on-the-table--953844116-5a911b6ab4974a738b7a3c7e79a63ad0.jpg)
_HOOK_
What are the potential benefits of implementing a negative income tax system?
One potential benefit of implementing a negative income tax system is that it can provide a safety net for low-income individuals and families, helping to alleviate poverty. By providing financial assistance to those below a certain income level, the negative income tax ensures that everyone has a minimum level of income to meet their basic needs.
Another potential benefit is that it simplifies the welfare system. Unlike traditional welfare programs, which often come with complex eligibility requirements and administrative burdens, a negative income tax system operates through the tax system. This can streamline the process and reduce bureaucratic red tape, making it easier for individuals to access the support they need.
Furthermore, a negative income tax system can provide work incentives. Under this system, individuals are still encouraged to work and earn income, as the financial assistance decreases gradually as income increases. This can incentivize individuals to seek employment or engage in entrepreneurial endeavors, ultimately leading to increased labor force participation and economic productivity.
Additionally, implementing a negative income tax system can help reduce income inequality. By providing financial support to those with low incomes, it can help bridge the wealth gap and promote a more equitable distribution of resources. This can contribute to social stability and cohesion in society.
Moreover, a negative income tax system can potentially reduce the administrative costs associated with welfare programs. Traditional welfare programs often require significant resources for administration and enforcement, while a negative income tax system can operate more efficiently through the existing tax infrastructure, potentially resulting in cost savings.
Overall, the potential benefits of implementing a negative income tax system include reducing poverty, simplifying the welfare system, providing work incentives, reducing income inequality, and potentially decreasing administrative costs. It is important to note, however, that the actual impact and success of such a system would depend on its design, implementation, and the specific context in which it is implemented.
Are there any countries that currently utilize a negative income tax system?
Yes, there are countries that currently utilize a negative income tax system. One prominent example is the United States. The concept of a negative income tax was first introduced by economist Milton Friedman in the 1960s as a way to address poverty and income inequality. However, the negative income tax system has not been fully implemented in the US.
Instead, the US has implemented elements of the negative income tax system through programs like the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). The EITC provides a refundable tax credit to low-income individuals and families, effectively reducing their tax liability and potentially resulting in a negative tax. This means that instead of paying taxes, eligible individuals receive money from the government as a form of income support.
Other countries have experimented with similar concepts and have implemented their own versions of negative income tax or income guarantee programs. For example, Finland and Canada have conducted pilot programs to test the feasibility and effectiveness of providing a basic income or negative income tax to their citizens. These pilots aim to provide a minimum income level to individuals, regardless of whether they have a job, in an effort to alleviate poverty and improve social welfare.
It is worth noting that the specific design and implementation of a negative income tax system can vary between countries. Some countries may opt for a full-scale negative income tax system, while others may have partial implementations or pilot programs. The goal remains the same, which is to provide financial support to individuals and families with low or no income, ultimately reducing poverty and income inequality.
How does a negative income tax proposal suggest replacing welfare with refundable tax credits?
A negative income tax proposal suggests replacing the traditional welfare system with refundable tax credits. Here is a step-by-step explanation of how this would work:
1. Income Threshold: The negative income tax system sets a threshold below which individuals or households are considered to have \"negative income\" or an income below a certain level. This threshold is typically set at the poverty line or a similar measurement of low income.
2. Refundable Tax Credits: Instead of receiving welfare benefits directly, individuals or households with income below the threshold would receive refundable tax credits from the government. These tax credits are refundable, meaning that if the amount of credit exceeds the individual\'s tax liability, the excess amount is paid out as a cash refund.
3. Progressive Reduction: As income increases above the threshold, the refundable tax credits gradually decrease, creating a progressive reduction in the amount of support received. This ensures that the system provides assistance to those who need it the most.
4. Simplified Administration: By using the existing tax system to deliver support, the negative income tax proposal aims to simplify the administration process. Instead of relying on multiple welfare programs and eligibility criteria, individuals or households only need to file their tax returns to receive the refundable tax credits.
5. Incentives for Work: One of the key advantages of a negative income tax system is that it provides incentives for individuals to work. Unlike the traditional welfare system, where individuals may face a sharp reduction in benefits as their income increases through work, the refundable tax credits gradually decrease, allowing individuals to keep a larger portion of their earnings. This helps to alleviate the \"welfare trap\" and encourages higher workforce participation.
6. Cost and Implementation: The cost of implementing a negative income tax system would depend on various factors such as the income threshold, the level of refundable tax credits, and the number of eligible individuals. It would require careful consideration and analysis to determine the financial feasibility and implementation process of such a system.
Overall, the negative income tax proposal suggests a shift from traditional welfare programs to a tax-based approach, where individuals or households with low incomes receive refundable tax credits. This system aims to provide a more streamlined and progressive means of assistance, while also encouraging work and reducing bureaucratic complexity.
Negative Income Tax Explained - The Answer to Welfare - Milton Friedman
Curious about the connection between the Negative Income Tax and welfare programs? This enlightening video provides a comprehensive explanation of how this tax system can redefine the way we approach social assistance. Witness how the Negative Income Tax offers a flexible and empowering solution that ensures a safety net for all citizens. Join us in reimagining the future of welfare.
What is Negative Income Tax? Canara HSBC Life Insurance
Confused about the concept of Negative Income Tax? Canara HSBC Life Insurance is here to demystify it in this informative video. Discover how this progressive tax system can foster financial security and support individuals in building a better tomorrow. Don\'t miss this opportunity to learn about this unique approach and how it aligns with Canara HSBC Life Insurance\'s values of empowerment and financial well-being.
What is the basic income guarantee and how does it relate to negative income tax?
The basic income guarantee is a system that ensures every individual receives a certain minimum income, regardless of their employment status or level of income. It is an unconditional payment made to all citizens or residents of a country.
The negative income tax, on the other hand, is a specific policy proposal that can be used to implement the basic income guarantee. It suggests that individuals below a certain income level should receive money from the government instead of paying taxes. In essence, it aims to provide financial assistance to those who fall below a designated income threshold.
The basic income guarantee and negative income tax are closely related in that they both aim to alleviate poverty and ensure a minimum level of income for all citizens. The negative income tax is a means to achieve the basic income guarantee by modifying the existing tax system. It essentially transforms the tax system from one that collects money from individuals to one that provides financial support to those in need.
Under a negative income tax system, individuals below the designated income threshold would receive money from the government in the form of a tax credit or refundable credit. The amount received would depend on their income level and would gradually decrease as their income rises. This ensures that individuals have a certain level of income to meet their basic needs and acts as a form of social safety net.
Implementing a basic income guarantee through a negative income tax requires careful consideration of income thresholds, tax rates, and funding mechanisms. It also raises important questions about economic incentives and the redistribution of wealth. Nonetheless, both concepts aim to address income inequality and provide a safety net for those in need.

READ MORE:
What are some potential criticisms or challenges associated with implementing a negative income tax system?
1. Disincentive to work: One of the main criticisms of a negative income tax system is that it may create a disincentive for individuals to work. Since individuals would receive income even if they do not work, some argue that it could lead to decreased motivation and effort to seek employment or increase one\'s earnings.
2. Administrative burden: Implementing a negative income tax system would require a significant administrative effort. Determining eligibility and accurately calculating and distributing payments to individuals could be complex and costly. Ensuring that the system is effective and efficient could be a challenge for governments.
3. Potential for abuse: Another concern is the possibility of individuals exploiting the system by providing false information about their income levels to receive more benefits. Proper monitoring and enforcement would be necessary to prevent abuse and ensure that only those who truly need assistance are eligible for the benefits.
4. Funding concerns: Implementing a negative income tax system would require significant financial resources. Critics argue that such a system could lead to increased government spending, requiring higher taxes or increased government debt. Evaluating the feasibility and sustainability of funding such a system is a valid concern.
5. Impact on labor market: Some argue that a negative income tax system may disrupt the labor market by artificially influencing wages. If individuals can rely on income from the government, employers may have less pressure to increase wages, which could negatively impact workers\' bargaining power and overall wages.
6. Complexity and potential for unintended consequences: Developing a well-designed and effective negative income tax system is a complex task. It involves setting income thresholds, determining benefit amounts, and addressing various potential scenarios. There is a risk of unintended consequences, such as unintended redistribution of wealth or unintended effects on labor supply and market dynamics.
It is important to note that while these criticisms exist, proponents of negative income tax argue that it can provide a more streamlined and effective approach to poverty alleviation and income redistribution. The challenges associated with implementation need to be carefully considered and addressed to ensure the success of such a system.
_HOOK_




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TaxableIncome_Final_4188122-0fb0b743d67242d4a20931ef525b1bb1.jpg)