Topic what is income tax in michigan: Income tax in Michigan refers to the mandatory levy imposed by the state on individuals\' earned income. This tax plays a crucial role in funding public services and infrastructure developments, ensuring a higher quality of life for Michigan residents. By contributing to income tax, individuals contribute to the growth and prosperity of their state. Understanding income tax regulations and seeking assistance when needed can help citizens fulfill their tax obligations efficiently and effectively, leading to a smoother tax filing process.
Table of Content
- What is the income tax rate in Michigan?
- What is the income tax rate in Michigan?
- Are there any exemptions or deductions available for Michigan income tax?
- YOUTUBE: Living on $100,000 After Taxes in Michigan
- How is Michigan income tax calculated?
- Is Michigan income tax progressive or flat?
- Are there any special tax credits or incentives for Michigan residents?
- Are Social Security benefits taxable in Michigan?
- Do non-residents have to pay income tax in Michigan?
- Are there any additional local taxes imposed on income in Michigan?
- How can I file my Michigan income tax return?
What is the income tax rate in Michigan?
The income tax rate in Michigan is a flat tax rate of 4.25% for individuals and businesses. This means that regardless of income, everyone is taxed at the same rate. However, it is important to note that there may be additional local income taxes imposed by some cities or municipalities within Michigan.
To calculate your income tax in Michigan, you can follow these steps:
1. Determine your taxable income: Start by calculating your total income from all sources, including wages, salaries, tips, business income, rental income, and any other taxable income. Deduct any applicable adjustments or deductions allowed by Michigan tax laws.
2. Apply the flat tax rate: Once you have determined your taxable income, multiply it by the tax rate of 4.25%. This will give you the amount of income tax you owe to the state of Michigan.
3. Consider additional local taxes: As mentioned earlier, some cities or municipalities in Michigan may levy additional income taxes. If you live or work in an area with local income taxes, you will need to factor those in separately. Check with the specific local taxing authorities for their rates and rules.
4. Determine your tax liability: Subtract any applicable tax credits, exemptions, or deductions from your calculated income tax amount. These may include credits such as the Michigan Homestead Property Tax Credit or other allowable deductions. The final result will be your total income tax liability for the year.
It\'s always recommended to consult with a tax professional or refer to Michigan Department of Treasury\'s official website for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding income taxes in Michigan.

READ MORE:
What is the income tax rate in Michigan?
The income tax rate in Michigan depends on your taxable income and filing status. As of 2022, Michigan has a flat income tax rate of 4.25% for all individuals, regardless of their income level. Here\'s how you can calculate your income tax in Michigan:
1. Determine your taxable income: Start by calculating your total income for the year, including wages, salaries, tips, self-employment income, and any other sources of income. Subtract any allowable deductions and exemptions to arrive at your taxable income.
2. Identify your filing status: Determine whether you will be filing as a single individual, married filing jointly, married filing separately, or as head of household. Your filing status affects the tax brackets and deductions available to you.
3. Calculate your income tax: Once you have your taxable income and filing status determined, you can use the Michigan income tax rate of 4.25% to calculate your income tax. Multiply your taxable income by 0.0425 (4.25% expressed as a decimal) to find out your income tax liability.
4. Consider any additional taxes or credits: Keep in mind that besides the state income tax, you may also be subject to other taxes, such as local income taxes or federal income taxes. Additionally, you may be eligible for various tax credits and deductions that can reduce your overall tax liability.
It\'s important to note that tax laws and rates can change over time, so it\'s always a good idea to consult the official Michigan Department of Treasury website or consult with a tax professional for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding income tax rates in Michigan.
Are there any exemptions or deductions available for Michigan income tax?
Yes, there are exemptions and deductions available for Michigan income tax. Here are some of the most common ones:
1. Personal Exemptions: Michigan allows for personal exemptions for taxpayers and their dependents. The exemption amount is based on the taxpayer\'s filing status. As of 2021, the exemption amounts are $4,650 for single filers and married individuals filing separately, $9,300 for married couples filing jointly, and $4,650 for each dependent.
2. Standard Deduction: Michigan offers a standard deduction for those who do not itemize their deductions. The standard deduction amount varies based on filing status. For tax year 2021, the standard deduction amounts are $4,900 for single filers and married individuals filing separately, and $9,800 for married couples filing jointly.
3. Itemized Deductions: If you choose to itemize your deductions, Michigan allows deductions for various expenses such as medical expenses, state and local taxes, mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and certain education expenses. However, it\'s important to note that Michigan follows different rules from the federal government when it comes to itemized deductions, so it\'s essential to consult the Michigan Department of Treasury or a tax professional for specific guidance.
4. Retirement Income Deduction: Michigan provides a retirement income deduction for individuals age 67 or older or those who are permanently and totally disabled. The deduction amount varies based on filing status and income. For tax year 2021, the maximum deduction is $54,810 for single filers and $109,620 for joint filers.
5. Michigan Educator Expense Deduction: Qualified educators in Michigan can deduct up to $20,000 for unreimbursed classroom supplies and educational materials used in their work.
These are just a few examples of exemptions and deductions available for Michigan income tax. It\'s important to note that tax laws can change, so it\'s recommended to consult the Michigan Department of Treasury or a tax professional for the most up-to-date and accurate information regarding your specific situation.
Living on $100,000 After Taxes in Michigan
Looking for ways to maximize your income? Watch this informative video on income tax to learn about deductions, credits, and strategies to minimize your tax liability. Take charge of your financial future and unlock the secrets to earning more and keeping more of your hard-earned money!
Michigan Income Tax Cut Expected for 2023 as Legislature Considers Additional Reform
Want to put more money back into your pocket? Don\'t miss this video on tax cuts that could potentially save you thousands of dollars. Discover the latest updates on tax legislation and uncover valuable tips on how to take advantage of these opportunities to reduce your tax burden.
How is Michigan income tax calculated?
To calculate your Michigan income tax, follow these steps:
1. Determine your taxable income: Start by calculating your total income for the year. This includes wages, tips, self-employment income, rental income, and other sources of taxable income. Subtract any deductions or exemptions you may qualify for, such as business expenses, student loan interest, or retirement contributions. The resulting amount is your taxable income.
2. Determine your tax rate: Michigan\'s individual income tax rates are a flat rate of 4.25%. Unlike federal income tax, Michigan does not have different tax brackets based on income levels.
3. Calculate your tax liability: Multiply your taxable income by the tax rate of 4.25% to find your Michigan income tax liability. For example, if your taxable income is $50,000, your tax liability would be $50,000 x 4.25% = $2,125.
4. Consider any credits or deductions: Michigan offers various tax credits and deductions that can potentially reduce your tax liability. For instance, you may be eligible for the Homestead Property Tax Credit if you own a home in Michigan. Make sure to review these options and determine if you qualify for any deductions or credits to reduce your tax liability.
5. File your tax return: Once you have calculated your tax liability and accounted for any credits or deductions, file your Michigan income tax return. You can do this online through the Michigan Department of Treasury\'s website or by mailing a paper return. Include any necessary forms and documentation to support your tax calculations and claimed credits or deductions.
It\'s important to note that tax laws and regulations can change, so it\'s always best to consult with a tax professional or refer to the most up-to-date information from the Michigan Department of Treasury to ensure accurate calculations and compliance with tax laws.
Is Michigan income tax progressive or flat?
Michigan income tax is progressive. This means that the tax rate increases as the taxable income increases. There are four income tax brackets in Michigan, each with its own tax rate:
1. For individuals with a taxable income of up to $19,050 (or married couples filing jointly with a taxable income of up to $38,100), the tax rate is 4.25%.
2. For individuals with a taxable income between $19,050 and $38,100 (or married couples filing jointly with a taxable income between $38,100 and $76,200), the tax rate is 4.35%.
3. For individuals with a taxable income between $38,100 and $86,650 (or married couples filing jointly with a taxable income between $76,200 and $173,300), the tax rate is 4.75%.
4. For individuals with a taxable income of $86,650 and above (or married couples filing jointly with a taxable income of $173,300 and above), the tax rate is 4.9%.
It\'s important to note that these tax rates are applicable for the 2022 tax year and may be subject to change in the future. Additionally, there may be additional deductions and credits available that can impact the overall tax liability in Michigan.

_HOOK_
Are there any special tax credits or incentives for Michigan residents?
Yes, there are several special tax credits and incentives available for Michigan residents. Some of them include:
1. Homestead Property Tax Credit: This credit is available to homeowners who have a household income below a certain threshold. It provides a refundable credit based on the property taxes paid on their primary residence.
2. Michigan Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): This credit is designed to help low-income working individuals and families. It is a refundable credit based on a percentage of the federal EITC.
3. Home Heating Credit: This credit assists eligible Michigan residents with their winter heating expenses. It is available to both homeowners and renters who meet certain income and residency requirements.
4. Small Business Tax Incentives: Michigan offers various tax incentives to small businesses to encourage growth and job creation in the state. These incentives may include tax credits for hiring and training employees, investment incentives, and incentives for locating in certain designated areas.
5. Film and Digital Media Production Credits: Michigan has a program that provides tax incentives for qualifying film and digital media productions in the state. These credits can offset a portion of the production costs incurred in Michigan.
Please note that the availability and details of these tax credits and incentives may vary, and it\'s always recommended to consult with a tax professional or the Michigan Department of Treasury to ensure you are eligible and understand the requirements for each credit or incentive.
Are Social Security benefits taxable in Michigan?
Yes, Social Security benefits can be taxable in Michigan. Here is a step-by-step explanation:
1. Determine your filing status: The first step is to determine your filing status. This can be either single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, head of household, or qualifying widow(er) with dependent child.
2. Calculate your provisional income: Provisional income includes not only your Social Security benefits but also other taxable income sources such as wages, pensions, dividends, and interest. To calculate your provisional income, add up all these sources of income.
3. Apply the taxability thresholds: Michigan follows the same taxability thresholds as the federal government. If your provisional income is below the threshold, your Social Security benefits are not taxable. If your provisional income exceeds the threshold, a portion of your Social Security benefits may be taxable.
4. Determine the taxable portion of your Social Security benefits: To determine the taxable portion of your Social Security benefits, you need to use a specific formula. This formula takes into account your filing status and the amount of your provisional income that exceeds the taxability thresholds. The Michigan Department of Treasury provides a worksheet (MI-1040CR) to help taxpayers calculate this.
5. Report the taxable portion: On your Michigan income tax return (Form MI-1040), you will need to report the taxable portion of your Social Security benefits. Make sure to follow the instructions provided by the Michigan Department of Treasury to correctly report this amount.
6. Determine your Michigan income tax liability: Finally, you will calculate your Michigan income tax liability based on your total taxable income, including any taxable portion of your Social Security benefits. Refer to the Michigan income tax brackets and rates, which can be found on the Michigan Department of Treasury website, to determine your tax liability.
Note: It is advisable to consult with a tax professional or refer to the Michigan Department of Treasury\'s official resources for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding the taxability of Social Security benefits in Michigan.

Do non-residents have to pay income tax in Michigan?
Non-residents may be required to pay income tax in Michigan if they have earned income from Michigan sources. Here is a step-by-step explanation:
1. Determine Residency Status: First, identify if you are a resident or a non-resident of Michigan. Residents are individuals who have established their permanent home in Michigan. Non-residents, on the other hand, are individuals who do not have a permanent home in Michigan but have earned income from Michigan sources.
2. Source of Income: If you have earned income from Michigan sources, such as wages from working in Michigan or rental income from properties located in Michigan, you may be subject to Michigan income tax as a non-resident.
3. Filing Requirements: Non-residents who have earned income from Michigan sources and meet certain income thresholds are generally required to file a Michigan income tax return. As of now, the income threshold for non-residents to file a Michigan income tax return is $1,000 or more.
4. Filing Process: To file your Michigan income tax return as a non-resident, you will need to use the appropriate forms. The most commonly used form is the MI-1040NR for non-residents. You will need to report your income earned in Michigan on this form and calculate your tax liability accordingly.
5. Tax Calculation: Michigan uses a graduated income tax rate, which means that the tax rate increases as income levels rise. Non-residents will need to calculate their tax liability based on the applicable tax brackets and rates provided by the Michigan Department of Treasury.
6. Tax Credits and Deductions: Non-residents may be eligible for certain tax credits and deductions in Michigan, similar to residents. These can help reduce your overall tax liability. Some common deductions and credits include the personal exemption, homestead property tax credit, and child care credit.
7. Paying Taxes: Once you have calculated your tax liability, you will need to pay the taxes owed to the Michigan Department of Treasury. There are various payment methods available, including electronic payments and check payments.
It is important to note that tax laws can change, and it is always recommended to consult with a tax professional or directly with the Michigan Department of Treasury for the most up-to-date and accurate information regarding your specific situation.
Michigan Families Can Start Filing State Income Tax Returns on Monday: What to Know
Confused about the filing process? This video will demystify the complexities of tax filing, guiding you step-by-step through the process. Learn about the forms you need, the deadlines to meet, and how to ensure your taxes are accurately filed, giving you peace of mind and avoiding unnecessary penalties.
Michigan Senate Approves $1B in Tax Cuts
Are you aware of the potential benefits of tax cuts for your financial situation? Get informed about the latest tax cuts being implemented and their impact on your wallet by watching this eye-opening video. Don\'t miss out on the opportunity to learn how these cuts can positively affect your financial future.
Are there any additional local taxes imposed on income in Michigan?
Yes, there are additional local taxes imposed on income in Michigan. Michigan has a state income tax, but some cities and municipalities also have their own local income taxes. These local income taxes are separate from the state income tax and are imposed in addition to it.
To determine if there are any additional local taxes imposed on income in Michigan, you can follow these steps:
1. Start by reviewing the information provided by the Michigan Department of Treasury. The department\'s website (https://www.michigan.gov/treasury) offers resources and guidance related to income taxes in Michigan.
2. Look for specific information on local income taxes. The Michigan Department of Treasury website should provide details on which cities and municipalities have local income taxes and what the tax rates are.
3. Alternatively, you can contact the Michigan Department of Treasury directly for accurate and up-to-date information. You can submit an inquiry through their eService or call their helpline at 517-636-4486.
4. When contacting the Michigan Department of Treasury, be prepared to provide your specific location or the city where you live or work. This will help them give you the most relevant and accurate information regarding any local income taxes that may apply to you.
Remember, it\'s important to stay informed about both state and local income taxes in Michigan to ensure that you comply with all tax obligations and avoid any penalties or fines.
READ MORE:
How can I file my Michigan income tax return?
To file your Michigan income tax return, you can follow these steps:
1. Gather all the necessary documents and information: Before you start filing your tax return, make sure you have collected all the relevant paperwork. This includes your W-2 forms, 1099 forms, records of any deductions or credits you plan to claim, and any other income-related documents.
2. Determine your filing status: In Michigan, you will need to determine your filing status. This can be single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, or head of household. Your filing status will affect your tax rate and deductions.
3. Choose your preferred method of filing: Michigan offers three options for filing your income tax return. You can file electronically through the Michigan Department of Treasury\'s e-filing system, use commercial software approved by the state, or file a paper return by mailing it to the Michigan Department of Treasury.
4. Complete the required forms: If you choose to file electronically, the e-filing system will guide you through the necessary forms and calculations. If you are using approved commercial software, follow the instructions provided by the software. If you decide to file a paper return, download the appropriate forms, such as the MI-1040 form for individual income tax, from the Michigan Department of Treasury\'s website. Fill out the forms accurately and legibly.
5. Calculate your income tax liability: Use the provided forms or software to calculate your Michigan income tax liability. Take into account any deductions, exemptions, and credits applicable to your situation.
6. Double-check your return: Ensure that all the information you entered is correct and matches your supporting documents. Mistakes or errors could delay processing of your return or result in penalties.
7. File your return: If you are filing electronically, follow the instructions provided by the e-filing system or software. If you are filing a paper return, make a copy for your records, sign the original, and mail it to the Michigan Department of Treasury at the address provided on the forms.
8. Pay any taxes owed or claim a refund: If you owe taxes, include the payment with your return. If you expect a refund, you can choose to have it directly deposited into your bank account or receive a paper check.
9. Keep copies and records: After filing your Michigan income tax return, make copies of all the documents and keep them for your records. This includes your filed tax return, supporting documents, and any correspondence related to your return.
10. Follow up if necessary: If you have any questions or need assistance, you can contact the Michigan Department of Treasury through the IIT eService or by phone at 517-636-4486.
Remember that this guide provides a general outline, and it\'s essential to consult the official resources from the Michigan Department of Treasury or seek professional tax advice specific to your situation.
_HOOK_


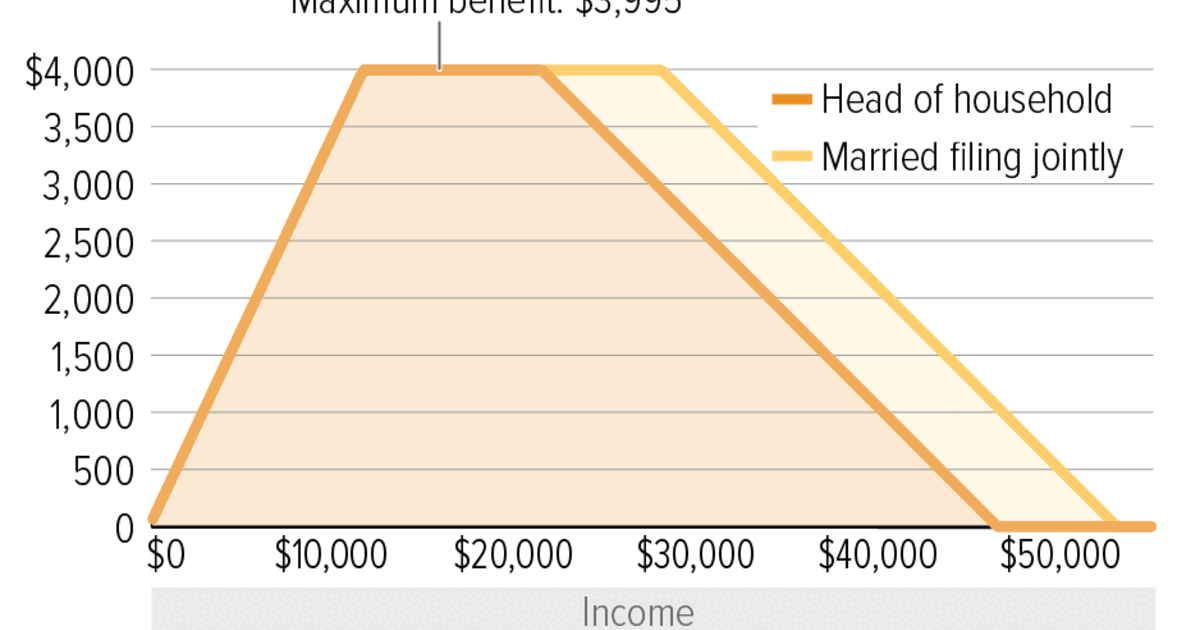


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/deferredincometax-v3-b8dc55e780ab4f47a0987161ece97060.png)





