Topic how to find the critical value for a confidence interval: Finding the critical value for a confidence interval is a crucial step in statistical analysis. By using the formula and reference data provided, you can easily determine the critical probability. This information allows you to establish the upper and lower bounds of your confidence interval with confidence. Mastering this technique empowers you to make informed decisions, effectively analyze data, and draw accurate conclusions with a desired level of certainty.
Table of Content
- How to calculate the critical value for a confidence interval?
- What is a critical value in the context of a confidence interval?
- How is the critical value related to the confidence level?
- YOUTUBE: How to find a critical value for a confidence level
- What is the equation to calculate the critical probability?
- How can the critical value be expressed in terms of confidence level?
- How do you calculate the alpha level from the confidence level?
- What is the significance of converting the alpha level to a decimal?
- How is the critical value determined for a hypothesis test?
- Is the confidence level the same as the significance level? If not, what is the relationship between them?
- Are confidence intervals and hypothesis tests linked in terms of their critical values?
How to calculate the critical value for a confidence interval?
To calculate the critical value for a confidence interval, follow these steps:
1. Determine the desired confidence level: The confidence level represents the level of certainty you want in your estimate. It is usually expressed as a percentage, such as 90%, 95%, or 99%.
2. Convert the confidence level to a significance level: The significance level (Alpha) is the complement of the confidence level. In other words, it is equal to 1 minus the confidence level divided by 100. For example, if the confidence level is 95%, the significance level would be 1 - (95 / 100) = 0.05.
3. Determine the critical probability (p*): The critical probability is calculated as 1 minus half the significance level. So, p* = 1 - (Alpha / 2).
4. Find the critical value: The critical value is the point on a standard normal distribution that corresponds to the critical probability. You can find this value using a standard normal distribution table or a statistical calculator.
5. Note the direction of the confidence interval: Depending on the type of confidence interval (two-tailed, upper-tailed, or lower-tailed), you may need to adjust the critical value accordingly. For a two-tailed interval, you would split the significance level evenly between the lower and upper tails, whereas for a one-tailed interval, the entire significance level would be used in one tail.
6. Apply the critical value to calculate the confidence interval: Once you have the critical value, you can use it in conjunction with the sample mean, standard deviation, and sample size to calculate the confidence interval. The formula for the confidence interval depends on the type of data and the known distribution assumed.
It\'s important to note that the specific calculation method may vary depending on the type of confidence interval needed and the distribution assumed. Make sure to adapt the method according to the specific requirements of your problem.

READ MORE:
What is a critical value in the context of a confidence interval?
In the context of a confidence interval, a critical value is a specific value that is used to determine the range of values within which a parameter is likely to lie. It plays a crucial role in constructing a confidence interval.
When calculating a confidence interval, we need to consider the level of confidence desired. The level of confidence represents the percentage of confidence we have that the true parameter falls within the interval.
To find the critical value for a confidence interval, follow these steps:
1. Determine the level of confidence desired. For example, if you want a 95% confidence interval, the level of confidence would be 95%.
2. Convert the level of confidence to a significance level (α). The significance level is the probability of making a Type I error (rejecting a true null hypothesis). It is equal to 1 minus the level of confidence divided by 100. For example, for a 95% confidence interval, the significance level would be 1 - (95/100) = 0.05.
3. Depending on the distribution of the data or the sample size, you will use different tables or formulas to find the critical value. For example, if you are working with a normal distribution and have a large sample size, you can use the z-table to find the critical value. The z-table provides the value at which a certain proportion of the distribution falls below that value. The critical value corresponds to the proportion of the distribution outside the confidence interval.
4. Look up the critical value in the appropriate table or use a statistical calculator. This value will correspond to the desired level of confidence and will be specific to the distribution and sample size.
5. Multiply the critical value by the standard deviation of the sample or, if the population standard deviation is known, by the standard error of the mean. This will give you the margin of error, which is the range of values that will be added/subtracted from the sample mean to create the confidence interval.
6. Finally, construct the confidence interval by subtracting the margin of error from the sample mean for the lower bound and adding the margin of error to the sample mean for the upper bound.
It is important to note that the critical value is influenced by the level of confidence, the distribution of the data, and the sample size. These factors should be taken into consideration when finding the critical value for a confidence interval.
How is the critical value related to the confidence level?
The critical value is closely related to the confidence level in a confidence interval. The confidence level represents the degree of certainty or reliability that we have in the estimate of a population parameter.
To find the critical value for a confidence interval, you first need to determine the confidence level you want to use. This is typically expressed as a percentage, such as 95% or 90%.
Once you have the confidence level, you subtract it from 100% to find the significance level (alpha). For example, if you have a 95% confidence level, the significance level would be 100% - 95% = 5%.
Next, you convert the significance level to a decimal value. In this case, 5% becomes 0.05.
The critical value is then calculated using the formula: Critical value (CV) = 1 - (alpha/2). The alpha/2 represents half of the significance level.
For instance, if the significance level is 0.05, you divide it by 2 to get 0.025. Subtracting this value from 1 gives you the critical value.
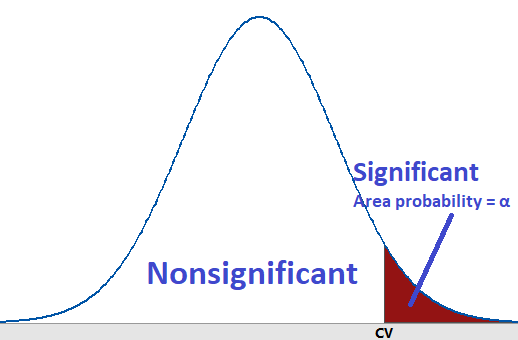
The critical value is important because it determines the range around the sample statistic within which the true population parameter is likely to fall. It is used to calculate the margin of error in a confidence interval. The larger the critical value, the wider the interval and the greater the confidence in the estimate.
In summary, the critical value is directly related to the confidence level. It is calculated using the significance level, which is derived from the confidence level. The critical value determines the width of the confidence interval and affects the level of confidence we have in our estimate.
How to find a critical value for a confidence level
Boost your confidence level with these effective tips! Learn how to overcome self-doubt and step into your full potential in this empowering video. Gain the reassurance you need to conquer any challenge that comes your way and unleash your true capabilities!
What is the equation to calculate the critical probability?
To calculate the critical probability for a confidence interval, you can use the following equation:
Critical probability (p*) = 1 - (Alpha / 2)
Where:
- Alpha represents the significance level or the level of confidence chosen for the interval.
- Divide Alpha by 2 to account for a two-tailed test.
To obtain the critical value, you will need to use the confidence level to determine Alpha. The confidence level is typically expressed as a percentage, such as 90%, 95%, or 99%.
Step-by-step process:
1. Determine the desired confidence level for the interval. Let\'s say you want a 95% confidence level.
2. Subtract the confidence level from 100% to find the Alpha level. In this case, 100% - 95% = 5%.
3. Convert the Alpha level to a decimal by dividing it by 100. In this case, 5% = 0.05.
4. Divide the decimal Alpha by 2. For example, 0.05 / 2 = 0.025.
5. Subtract the result from 1 to find the critical probability. In this case, 1 - 0.025 = 0.975.
Therefore, the critical probability for a 95% confidence interval would be 0.975.
How can the critical value be expressed in terms of confidence level?
To express the critical value in terms of confidence level, you can follow these steps:
1. Determine the desired level of confidence for your interval. This is usually expressed as a percentage, such as 90%, 95%, or 99%.
2. Subtract the confidence level from 100% to find the complement. For example, if the desired confidence level is 95%, the complement would be 100% - 95% = 5%.
3. Convert the complement from step 2 into a decimal by dividing it by 100. In this case, 5% becomes 0.05.
4. Divide the result from step 3 by 2 to find the critical probability (p*). This is because the critical value is symmetrical around the center, and you\'re determining the value for one tail. For example, if p* = 0.025.
5. Calculate the critical value by finding the corresponding value from the appropriate statistical distribution table or using statistical software. The specific distribution table to use depends on the type of interval or hypothesis test you are performing (e.g., z-table for the standard normal distribution, t-table for the t-distribution).
Alternatively, if you know the specific distribution and its corresponding quantile function, you can use it to directly calculate the critical value.
Remember that the critical value determines the width of the confidence interval and accounts for the desired level of confidence. It is essential for estimating the range in which a population parameter is likely to fall.
_HOOK_
How do you calculate the alpha level from the confidence level?
To calculate the alpha level from the confidence level, follow these steps:
1. Determine the desired confidence level. For example, if you want a 95% confidence level, the remaining 5% is the significance level.
2. Subtract the confidence level from 100%. In this example, 100% - 95% = 5%.
3. Convert the result from step 2 into a decimal by dividing by 100. In our example, 5% is equal to 0.05.
4. The decimal obtained in step 3 represents the alpha level. In this case, the alpha level is 0.05.
So, in summary, to calculate the alpha level from the confidence level, subtract the confidence level from 100%, convert the result to a decimal by dividing by 100, and this decimal is your alpha level.
Critical value for a given confidence level | AP Statistics | Khan Academy
Struggling with AP Statistics? Look no further! Dive into this comprehensive video guide that simplifies complex concepts, making them easy to understand. Improve your understanding of statistical analysis and increase your chances of acing your AP Statistics exam!
Find Critical Value Z for Confidence Intervals with Table
Unlock the secrets hidden within data with the help of this video! Dive into the world of tables and learn how to effectively organize information for easy analysis. Whether you\'re a beginner or seeking to refine your skills, this video will make working with tables a breeze!
What is the significance of converting the alpha level to a decimal?
The significance of converting the alpha level to a decimal is to ensure consistency in calculations and statistical analysis.
In statistics, the alpha level represents the significance level or the probability of making a Type I error, which is the probability of rejecting a null hypothesis when it is actually true. Typically, the alpha level is expressed as a percentage, such as 5% or 0.05.
To calculate the confidence level and find the critical value for a confidence interval, it is necessary to convert the alpha level to a decimal. This is done to ensure uniformity in the calculations because many statistical formulas and tables use decimal values.
Converting the alpha level to a decimal simplifies equations and calculations by removing the need to manipulate percentages. It allows for more straightforward mathematical operations and facilitates the use of tables and statistical software that often require decimal values.
Converting the alpha level to a decimal also helps maintain consistency with other statistical tests and procedures. Many hypothesis tests, such as t-tests and z-tests, also use the alpha level to determine the critical value. By converting the alpha level to a decimal, it becomes easier to compare and interpret results from different statistical analysis techniques.
Overall, converting the alpha level to a decimal serves as a practical and standard practice in statistical analysis to ensure accuracy, consistency, and compatibility with various statistical methods and tools.

How is the critical value determined for a hypothesis test?
The critical value for a hypothesis test is determined based on the desired confidence level or the significance level, depending on the type of test.
1. Confidence Level: If you want to construct a confidence interval, the critical value is determined by the desired confidence level.
- Start by determining the level of confidence you want for your interval. For example, if you want a 95% confidence level, the level of significance (Alpha) would be 1 - (95/100) = 0.05.
- Next, find the critical probability (p*) by subtracting Alpha/2 from 1. For example, p* = 1 - (0.05 / 2) = 0.975.
- Finally, you would find the critical value associated with the critical probability using a statistical table or software specific to the distribution you are working with. For example, for a normal distribution, you would look up the z-score associated with 0.975.
2. Significance Level: If you want to perform a hypothesis test, the critical value is determined by the significance level (Alpha).
- Start by determining the level of significance you want for your test. For example, if you want a significance level of 0.05 (or 5%), then Alpha would be 0.05.
- Find the critical value associated with the significance level using a statistical table or software specific to the distribution you are working with. This critical value is often denoted by a specific z, t or chi-square score, depending on the test and distribution.
It\'s important to note that the critical value represents the boundary beyond which you would reject the null hypothesis. If your test statistic falls beyond this critical value, it provides evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
Remember to consult appropriate statistical tables or software to obtain the exact critical value based on the specific distribution and desired confidence level or significance level.
Is the confidence level the same as the significance level? If not, what is the relationship between them?
The confidence level and the significance level are not the same, but they are related to each other.
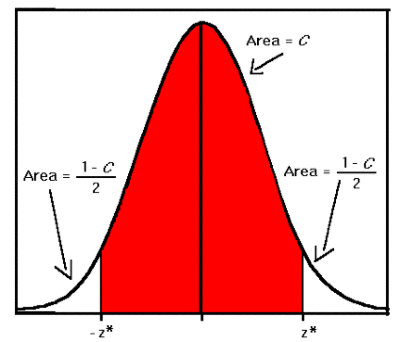
The confidence level refers to the probability that the true population parameter lies within the confidence interval. It is typically expressed as a percentage, such as 90%, 95%, or 99%. For example, a 95% confidence level means that if we were to repeat the sampling procedure many times and construct confidence intervals each time, approximately 95% of these intervals would contain the true population parameter.
On the other hand, the significance level, often denoted as α (alpha), is the criterion used to determine statistical significance in hypothesis testing. It represents the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true. Common values for the significance level are 0.05 (5%) and 0.01 (1%).
The relationship between the confidence level and the significance level is complementary. The confidence level and the significance level add up to 1. For example, a 95% confidence level corresponds to a significance level of 0.05 (1 - 0.95), and a 99% confidence level corresponds to a significance level of 0.01 (1 - 0.99).
In other words, if we set a higher confidence level, it means we are increasing our certainty that the true population parameter falls within the confidence interval. However, this also leads to a lower significance level and, therefore, a more stringent criterion for rejecting the null hypothesis in hypothesis testing. Conversely, if we set a lower confidence level, it means we have less certainty in the interval estimate, but it allows for a higher significance level and a less strict criterion for rejecting the null hypothesis.
Both the confidence level and the significance level are important considerations in statistical analysis and provide a balance between the level of uncertainty in estimation and the level of evidence required to reject a null hypothesis.
Are confidence intervals and hypothesis tests linked in terms of their critical values?
Yes, confidence intervals and hypothesis tests are indeed linked in terms of their critical values. Both confidence intervals and hypothesis tests are statistical techniques used to make inferences about population parameters based on sample data.
The critical value plays a crucial role in both these techniques. It represents the threshold value that is used to determine the acceptance or rejection of a null hypothesis. In hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis is assumed to be true, and the critical value is compared to the test statistic calculated from the sample data. If the test statistic falls within the rejection region defined by the critical value, the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of an alternative hypothesis.
Similarly, in the construction of a confidence interval, the critical value is used to determine the range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie. The confidence level chosen determines the size of the interval. The critical value is calculated based on the desired confidence level and the distribution of the sample data. Typically, it is derived from a standard probability distribution, such as the normal distribution or the t-distribution, depending on the nature of the data and assumptions made.
It\'s important to note that the critical values for both hypothesis tests and confidence intervals are determined based on the desired level of confidence or significance level chosen by the researcher. The confidence level represents the desired level of confidence in which the parameter is estimated to fall within the interval, while the significance level represents the probability of making a Type I error (rejecting a true null hypothesis).
In summary, both confidence intervals and hypothesis tests are linked through their use of critical values. The critical value helps determine decision rules for both techniques, aiding in the interpretation of results and making statistically valid inferences about population parameters.
_HOOK_
How To Find The Z Score Given The Confidence Level of a Normal Distribution
Decode the mysteries of Z scores by watching this informative video. Discover how to calculate and interpret Z scores with confidence, helping you to analyze data more accurately. Understand the power of Z scores and take your statistical analysis skills to the next level!
