Topic how to calculate p value using spss: Discover how to calculate the p-value using SPSS in just a few easy steps. SPSS, a powerful statistical software, provides a user-friendly interface to perform this calculation without any hassle. By utilizing the one-sample t-test command, you can determine if your test value is statistically significant compared to the population mean. Understanding and interpreting correlation in SPSS is made simpler through helpful tutorials and videos. Empower yourself with this knowledge and unlock the full potential of SPSS for your research and analysis.
Table of Content
- How do I calculate the p-value using SPSS?
- What is the purpose of calculating the p-value using SPSS?
- How can Pearson\'s correlation be calculated and interpreted using SPSS?
- YOUTUBE: Correlation in SPSS: P-Value
- Is it possible to calculate the t-value using SPSS? If so, how?
- How is a one-sample t-test performed using SPSS?
- Can SPSS be used to determine if a given population mean is statistically significant?
- What steps are involved in calculating the p-value using SPSS?
- Are there any specific commands or functions in SPSS for calculating p-values?
- Can SPSS calculate p-values for different types of statistical tests, such as chi-square or ANOVA?
- Are there any limitations or potential errors to be aware of when using SPSS to calculate p-values?
How do I calculate the p-value using SPSS?
To calculate the p-value using SPSS, you need to perform a statistical test, such as a t-test or ANOVA. Here is a general step-by-step guide to calculating the p-value using SPSS:
1. Open SPSS and load your data.
2. Go to \"Analyze\" in the top menu and choose the appropriate statistical test for your research question. For example, if you are comparing means between two groups, choose \"Compare Means\" and then \"Independent Samples t-test.\"
3. Select the variables you want to analyze and move them to the appropriate boxes in the dialog box.
4. Specify any additional options or settings needed for your analysis. For example, you may need to select whether your data is normally distributed or choose the type of t-test you want to perform (e.g., one-sample, independent samples, paired samples).
5. Click \"OK\" to run the analysis.
6. SPSS will provide you with the test statistics, such as the t-value or F-value, and the degrees of freedom.
7. To obtain the p-value, locate the test statistic (t-value or F-value) in the test distribution table or use the SPSS output directly. The p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as (or more extreme than) the one observed, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
8. If using the test distribution table, find the row corresponding to the degrees of freedom and the column corresponding to the test statistic. The value at the intersection represents the p-value.
9. Alternatively, if you are using SPSS, the p-value will be included in the output. Look for the \"Sig.\" or \"p\" value associated with your test statistic. This value indicates the probability (p-value) that the test statistic could have occurred by chance.
10. Interpret the p-value based on your predetermined significance level (e.g., 0.05). If the p-value is less than your significance level, you can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is a significant difference or relationship. If the p-value is greater than your significance level, you fail to reject the null hypothesis, indicating that there is no significant difference or relationship.
It\'s important to note that the exact steps may vary depending on the specific statistical test or analysis you are conducting in SPSS. Be sure to consult relevant resources or textbooks for more specific instructions on conducting your particular analysis.

READ MORE:
What is the purpose of calculating the p-value using SPSS?
The purpose of calculating the p-value using SPSS is to determine the statistical significance of a result in hypothesis testing. The p-value is a measure that quantifies the strength of evidence against the null hypothesis. It tells us the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as the one observed, or more extreme, given that the null hypothesis is true.
To calculate the p-value using SPSS, follow these steps:
1. Input your data into SPSS.
2. Choose the appropriate statistical test based on your research question and data. For example, if you are comparing means between two groups, you would use an independent samples t-test.
3. Conduct the statistical test in SPSS.
4. Look for the output that provides the test statistic and its associated p-value. The exact location of this information may vary depending on the test you are conducting in SPSS.
5. Interpret the p-value. If the p-value is less than or equal to your predetermined significance level (usually 0.05), then the result is considered statistically significant. This means that there is strong evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. If the p-value is greater than the significance level, then the result is not statistically significant, and there is insufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
Remember that the p-value is not an absolute measure of the strength or importance of the result, but rather a measure of evidence against the null hypothesis. The smaller the p-value, the stronger the evidence against the null hypothesis. It is important to consider the context of the research question and the practical significance of the results when interpreting the p-value.
How can Pearson\'s correlation be calculated and interpreted using SPSS?
To calculate and interpret Pearson\'s correlation using SPSS, you can follow these steps:
Step 1: Open SPSS and import your dataset by going to \"File\" and selecting \"Open\" or by clicking on the \"Open File\" button.
Step 2: Once the dataset is imported, go to \"Analyze\" in the top menu and select \"Correlate\" and then \"Bivariate\".
Step 3: In the \"Bivariate Correlations\" window, select the variables you want to calculate the correlation for by clicking on them and then clicking the arrow button to move them to the \"Variables\" box.
Step 4: Under the \"Options\" button, you can choose whether to calculate Pearson\'s correlation coefficient or other types of correlations. Make sure to select \"Pearson\" as the correlation coefficient.
Step 5: Click \"OK\" to run the correlation analysis.
Step 6: The output will show the correlation coefficient, its significance level (p-value), and other relevant statistics. Look for the value next to \"Pearson Correlation\" to find the correlation coefficient. The p-value will indicate the level of statistical significance.
Step 7: Interpret the results. If the correlation coefficient is close to -1 or 1, it indicates a strong correlation. A value close to 0 suggests a weak or no correlation. The p-value indicates the likelihood of obtaining the observed correlation coefficient by chance. If the p-value is less than 0.05 (assuming a significance level of 0.05), it suggests a statistically significant correlation.
Remember, interpretation should be based on the specific context of the variables being analyzed.
Correlation in SPSS: P-Value
Correlation: Discover the power of correlation and how it can unveil hidden relationships between variables. Watch our intriguing video to learn how to interpret correlation coefficients and confidently apply this statistical concept in your research or analysis.
Is it possible to calculate the t-value using SPSS? If so, how?
Yes, it is possible to calculate the t-value using SPSS. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to do it:
1. First, open your data file in SPSS and make sure the variable of interest is properly coded and entered into the program.
2. Go to the \"Analyze\" menu and select \"Compare Means\". From the dropdown menu, choose the appropriate test based on your research design. For example, if you are comparing means between two independent groups, select \"Independent Samples T Test\". If you are performing a one-sample t-test, select \"One-Sample T Test\".
3. In the new window that opens, select the variable you want to analyze from the list on the left and move it to the \"Test Variable(s)\" box on the right by clicking the arrow button.
4. If applicable, choose the appropriate grouping variable (e.g., if you are comparing means between two groups, select the grouping variable that identifies the groups). Move it to the \"Grouping Variable\" box.
5. Under the \"Options\" tab, make sure the \"Descriptive\" box is checked for additional information such as means and standard deviations.
6. Click \"OK\" to run the analysis.
7. SPSS will generate output with the results of your t-test. Look for the \"t-value\" column in the table. It represents the calculated t-value based on your data.
That\'s it! You can use this t-value to determine the statistical significance of your results by comparing it to the critical t-value associated with your chosen significance level.
How is a one-sample t-test performed using SPSS?
To perform a one-sample t-test using SPSS, follow these steps:
1. Open SPSS and import your data file or enter the data manually into SPSS.
2. Go to \"Analyze\" in the top menu and select \"Compare Means\" and then \"One-Sample T Test\".
3. In the \"One-Sample T Test\" dialog box, select the variable you want to test from the list of variables on the left and move it to the \"Test Variable(s)\" box on the right.
4. In the \"Test Value\" box, enter the value you want to compare the mean of the variable to. This could be a specific value or zero, depending on your research question.
5. Choose the desired level of significance (e.g., 0.05) in the \"Alpha\" box. This is the predetermined threshold for determining statistical significance.
6. Optionally, you can customize the output and change other settings in the dialog box.
7. Click \"OK\" to run the analysis.
8. SPSS will produce output that includes the test statistic (t-value), degrees of freedom, p-value, and other relevant information.
9. Look for the p-value in the output. If the p-value is less than the chosen significance level (e.g., 0.05), you can conclude that there is a statistically significant difference between the mean of the variable and the test value. If the p-value is greater than the significance level, you cannot reject the null hypothesis, which suggests that there is no significant difference.
Remember that it is important to interpret the results in the context of your research question and use caution in drawing conclusions solely based on statistical significance.

_HOOK_
Can SPSS be used to determine if a given population mean is statistically significant?
Yes, SPSS can be used to determine if a given population mean is statistically significant. Here are the step-by-step instructions:
1. Launch SPSS and open the dataset that contains the variable you want to test.
2. Go to \"Analyze\" in the menu bar and select \"Compare Means\".
3. From the drop-down menu, choose \"One-Sample T Test\" (assuming you want to compare the mean of a single variable to a specific value).
4. In the \"Test Variable(s)\" box, select the variable you want to test.
5. In the \"Test Value\" box, enter the specific value that you want to compare the mean to.
6. Click on the \"Options\" button to access additional settings, such as confidence intervals or assumed variances.
7. Click \"OK\" to run the analysis.
8. SPSS will generate an output table that includes the t-value, degrees of freedom, p-value, and other relevant statistics.
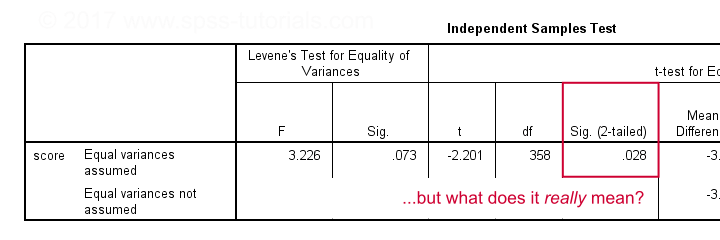
9. Look at the \"Sig. (2-tailed)\" value in the output table. This is the p-value associated with the test. If the p-value is less than your chosen significance level (e.g., 0.05), then you can conclude that the population mean is statistically significantly different from the test value.
It\'s important to note that these instructions are specific to comparing the mean of a single variable to a specific value using a one-sample t-test in SPSS. Other statistical tests or scenarios may require different procedures.
How to Calculate P Value in SPSS, Compare Two Variables in SPSS: Chi-Square Test and T-Test
Compare: Want to make informed decisions? Our video explores how to effectively compare different options or scenarios using insightful data analysis techniques. Uncover the secrets of making accurate comparisons and gain valuable insights that will guide your decision-making process.
T Test in SPSS: P-Value, Null Hypothesis, Written Results, APA Format (Part 1 of 2)
T-Test: Take a deep dive into the world of t-tests with our engaging video tutorial. Understand the fundamentals of this statistical test and learn how to execute it step-by-step. Gain the confidence to analyze your data and draw meaningful conclusions with this powerful statistical tool.
What steps are involved in calculating the p-value using SPSS?
To calculate the p-value using SPSS, you can follow the steps below:
1. Open your dataset in SPSS.
2. Click on \"Analyse\" in the top menu bar and then select the appropriate statistical test based on your research question. For example, if you want to conduct a t-test, select \"Compare Means\" and then \"Independent Samples T-Test.\"
3. In the dialogue box that appears, transfer your variables of interest to the appropriate boxes (e.g., transfer the dependent variable to the \"Test Variable(s)\" box and the group variable to the \"Grouping Variable\" box for a t-test).
4. Specify the appropriate test options and make sure to check the box that says \"Descriptives,\" as this will provide the mean values that are required for the calculation of the p-value.
5. Click on the \"Paste\" button at the bottom of the dialogue box, and select \"Descriptives\" from the drop-down list. This will generate syntax that includes the means of your variables.
6. Click on \"OK\" to run the analysis.
7. In the output window, locate the table that provides the means under the descriptives section.
8. Use the mean values to calculate the test statistic specific to your test. For example, for a t-test, subtract the means of the two groups and divide it by the standard error of the difference. The resulting value would be your test statistic.
9. Use the test statistic to determine the p-value. The exact method to calculate the p-value will depend on the specific statistical test you are conducting and its assumptions.
10. Finally, report the p-value in your results to determine the statistical significance of your findings.
Please note that these steps may vary slightly based on the specific analysis you are performing in SPSS. It is important to consult a statistics textbook or resource specific to your analysis to ensure accurate calculation and interpretation of the p-value.
Are there any specific commands or functions in SPSS for calculating p-values?
In SPSS, there are several commands and functions that can be used to calculate p-values.
1. One common way to calculate p-values in SPSS is by performing hypothesis tests, such as t-tests or ANOVA tests. These tests can be conducted using the \"Analyze\" menu and selecting the appropriate test under the \"Compare Means\" or \"General Linear Model\" options.
2. For t-tests, go to \"Analyze\" > \"Compare Means\" > \"Independent-Samples T Test\" or \"Paired-Samples T Test\" depending on the design of your study. In the dialog box, select your variables and specify the desired level of significance. Click \"OK\" and the output will include the p-value under the \"Sig.\" column.
3. For ANOVA tests, go to \"Analyze\" > \"General Linear Model\" > \"Univariate\" or \"Multivariate\" depending on the number of dependent variables. In the dialog box, select your independent and dependent variables, and specify the desired level of significance. Click \"OK\" and the output will include the p-value under the \"Sig.\" column for each effect.
4. Another way to calculate p-values in SPSS is by running regression analyses. The p-values for the regression coefficients can be found in the output under the \"Sig.\" column.
5. Additionally, SPSS also provides functions that allow you to calculate specific p-values. For example, the \"DESCRIBE\" command with the \"/TEST\" subcommand can be used to test a specific value against a variable\'s mean.
It is worth mentioning that the specific commands and functions may vary depending on the version of SPSS being used. Consulting SPSS documentation or online tutorials specific to your version of SPSS can provide more detailed step-by-step instructions.
Can SPSS calculate p-values for different types of statistical tests, such as chi-square or ANOVA?
Yes, SPSS can calculate p-values for different types of statistical tests, including chi-square and ANOVA. Here is a general step-by-step guide on how to calculate p-values for these tests using SPSS:
1. Open your dataset in SPSS and make sure the variables you want to analyze are correctly coded.
2. Go to the \"Analyze\" menu at the top of the SPSS window and select the appropriate test based on your research question. For example, for chi-square test, select \"Descriptive Statistics\" -> \"Crosstabs\". For ANOVA, select \"Compare Means\" -> \"One-Way ANOVA\".
3. In the dialog box that appears, move your variables to the appropriate sections (e.g., \"Rows\" and \"Columns\" for chi-square, or \"Dependent List\" for ANOVA).
4. Specify any additional options or settings based on your specific analysis. For example, for chi-square test, you might want to check the option for calculating expected cell counts or perform a post-hoc test; for ANOVA, you might want to specify the grouping variable or adjust for unequal variances.
5. Click \"OK\" to run the analysis.
6. Once the analysis is complete, SPSS will generate an output window with various tables and summary statistics. Look for the table that displays the test statistics and the p-values.
7. Interpret the p-value based on your research question and hypothesis. Typically, p-values less than or equal to 0.05 are considered statistically significant, indicating that the observed results are unlikely to have occurred by chance alone.
Remember, these steps provide a general overview of how to calculate p-values in SPSS for chi-square and ANOVA tests. Some details may vary depending on the specific version of SPSS or the analysis options chosen.
Are there any limitations or potential errors to be aware of when using SPSS to calculate p-values?
When using SPSS to calculate p-values, there are a few limitations and potential errors to be aware of:
1. Assumptions: SPSS assumes that the data follows certain assumptions depending on the statistical test being used. For example, the data should be normally distributed for parametric tests like t-tests and ANOVAs. Violating these assumptions can lead to inaccurate p-values.
2. Sample size: The accuracy of p-values depends on the sample size. Small sample sizes may lead to less accurate results and larger margins of error.
3. Type I error: SPSS calculates the p-value based on the assumption that there is truly no effect or difference between groups. This means that a significant p-value does not always guarantee a meaningful or practical result. It is important to consider the context and effect size in addition to the p-value.
4. Multiple comparisons: If you are conducting multiple tests or comparisons, the probability of obtaining a significant result by chance increases. This is known as the multiple comparisons problem, and it can lead to an increased number of false positives. Correcting for multiple comparisons, such as using Bonferroni adjustments or adjusting the alpha level, is important to avoid erroneous conclusions.
5. Missing data: SPSS may handle missing data differently depending on the analysis technique used. It is crucial to account for missing data appropriately to avoid biased or inaccurate p-values.
6. Interpretation: Understanding the meaning and interpretation of p-values is essential. A p-value alone does not provide information about the effect size, strength of the relationship, or practical importance of the findings. It is important to consider these factors along with the p-value when interpreting the results.
It is always recommended to consult with a statistician or an expert in statistical analysis to ensure accurate and reliable interpretation of results when using SPSS or any statistical software.
_HOOK_
Chi-Square Test in SPSS: Interpretation
Interpretation: Are you struggling to decipher complex data or research findings? Let our expert video guide you through the art of interpretation. Learn valuable strategies to make sense of intricate information and extract meaningful insights. Enhance your analytical skills and become a proficient interpreter of data with our insightful video.

